Lessico
Fulvio Orsini

Erudito
e bibliofilo italiano (Roma 1529-1600). Familiare![]() del cardinale Alessandro
Farnese, ne arricchì la biblioteca e le collezioni d'arte. La collezione dei
suoi libri e manoscritti, tra le più importanti del Cinquecento, fa ora parte
della Biblioteca Vaticana.
del cardinale Alessandro
Farnese, ne arricchì la biblioteca e le collezioni d'arte. La collezione dei
suoi libri e manoscritti, tra le più importanti del Cinquecento, fa ora parte
della Biblioteca Vaticana.
Antiquario e bibliotecario dei Farnese, Fulvio Orsini trascorre la sua esistenza dapprima al seguito del cardinale Ranuccio, poi, alla morte di questi, al servizio del fratello Alessandro (1520-1589) con il compito di curare l'ordinamento e lo sviluppo delle raccolte di antichità, di libri e manoscritti della famiglia. Autore di numerosi studi di carattere filologico, storico e antiquario, formerà una sua propria collezione di quadri, sculture, iscrizioni, monete, gemme. Un inventario redatto dall'Orsini poco prima della morte nel quale egli registra tutti i suoi beni artistici con l'indicazione del valore e del precedente proprietario, permette di valutare l'entità delle raccolte, destinate a passare nel 1600 in proprietà del cardinale Odoardo, nominato dall'Orsini stesso erede universale dei suoi beni.
Le antichità di Fulvio Orsini si ricongiungono in tal modo alle collezioni antiquarie di Alessandro Farnese, accrescendo così quel complesso di materiali destinato a costituire uno "Studio publico" offerto, insieme al patrimonio librario e artistico della famiglia, alla frequentazione di una più ampia cerchia di studiosi. Le monete, le iscrizioni, i marmi e le gemme di Fulvio Orsini sono oggi solo in parte identificabili nelle raccolte Farnese, conservate nel Museo Nazionale di Napoli.
Le gemme in particolare, in origine più di 400, dopo il loro trasferimento alla corte di Parma e la fusione col resto del Tesoro Farnese, furono in parte alienate o disperse; alcune sono oggi conservate nei musei di San Pietroburgo, Parigi, Londra, e in altre collezioni europee. Attualmente solo 80 di esse, tra gemme e cammei antichi e moderni, sono riconoscibili nella raccolta napoletana (sala X, vetrine 6-9).
Tra esse emergono alcuni capolavori della glittica di età ellenistica o augustea, talvolta firmati da noti maestri: il frammento di cammeo con la coppia di Centauri firmato da Sostratos, il cammeo di Athenion che raffigura Zeus in lotta con i Giganti e, ancora, la bellissima ametista con Artemide, opera di Apollonios. Accanto ai soggetti mitologici, numerose sono le gemme che raffigurano uomini illustri del passato - politici, filosofi, letterati - (sala X, vetrina 9) le cui sembianze l'Orsini aveva creduto di identificare sulla base delle effigi monetali e dei ritratti in marmo e in bronzo. Nella seconda metà del secolo XV era molto vivo l'interesse per la ritrattistica greca e romana, e l'opera di Orsini, le Imagines virorum illustrium pubblicate a Roma nel 1570, per i rigorosi intenti metodologici e il ricco apparato illustrativo, gli valse il titolo di "padre dell'iconografia antica".
www.cib.na.cnr.it

Ursijn: Fulvius Ursinus (Orsini), 1529-1600, een geleerde uit 't beroemde It. geslacht Orsini; van hem bestaat o.a. een werk: Imagines et elogia virorum illustrium et eruditorum ex antiquis lapidibus et numismatibus expressa. Hij zou ons dus op een camee de afbeelding van Vergilius bewaard hebben, die men op de titelprent in het schild ziet. Kardinaal was deze ‘Ursijn’ niet; de twee slotregels zijn later door Brandt en Vollenhove gewijzigd, zò dat het woord ‘Kardinael’ verdween; zie Poëzy II, 1682, blz. 336 en vergelijk een artikel van Dr. J.F.M. Sterck in De Zondagscourant van 11 Augustus 1929.
www.dbnl.org

Fulvio Orsini (December 11, 1529 - May 18, 1600) was an Italian humanist, historian, and archaeologist. He was a scion of the Orsini family, one of the oldest, most illustrious, and for centuries most powerful of the Roman princely families, whose origins, when stripped of legend, can be traced back to a certain Ursus de Paro, recorded at Rome in 998.
Orsini was the natural son probably of Maerbale Orsini of the line of Mugnano. Cast off by his father at the age of nine, he found a refuge among the choir boys of St. John Lateran, and a protector in Canon Gentile Delfini. He applied himself energetically to the study of the ancient languages, published a new edition of Arnobius and of the Septuagint, and wrote works dealing with the history of Rome.
Orsini brought together a large collection of antiquities, and built up a costly library of manuscripts and books, which later became part of the Vatican library . Orsini became also a friend and patron of El Greco, while the painter was in Rome (1570-1577). Orsini's collection would later include seven paintings by the artist (View of Mt. Sinai and a portrait of Clovio are among them).

Fara in Sabina (Rieti) - Palazzo Orsini
The Orsini family was one of the most celebrated princely families in medieval Italy and renaissance Rome, and which, in former times, had large possessions in Hungary. Members of the Orsini include popes Celestine III (1191-1198), Nicholas III (1277-1280), and Benedict XIII (1724-1730), numerous condottieri and other relevant political and religious figures.
Origins
According to their family lore, the Orsini are descended from the Julio-Claudian family of ancient Rome. This is fanciful, as well as the alleged connection to the German families of Anhalt, Baden and Rosenberg sporting the same name. The Orsini also carried on a political feud with the Colonna family until by Papal Bull it was stopped in 1511; in 1571 the Chiefs of both families married the nieces of Pope Sixtus V.
The Orsini were related to the Boboni family existing in Rome in the 11th century. The first members had in fact always doubled surname of Boboni-Orsini. This first known members is one Bobone, in the early 11th century, father of Pietro, in turn father of Giacinto dei Boboni (1110-1198), who in 1191 became pope as Celestine III. One of the first great nepotist popes, he created cardinals two of his nephews and allowed his cousin Giovanni Gaetano (Giangaetano, died 1232) to buy the fiefs of Vicovaro, Licenza, Roccagiovine and Nettuno, who formed the nucleus of the future territorial power of the family. The Boboni surname went lost with his children, who were called de domo filiorum Ursi. Two of them, Napoleone and Matteo Rosso the Great (1178-1246) increased considerably the prestige of the family. The former was the founder of the first southern line, who disappeared with Camillo Pardo in 1553. He obtained the city of Manoppello, later a countship, and was Papal gonfaloniere. Matteo Rosso, called the Great, was the effective lord of Rome from 1241, when he defeated the Imperial troops to 1243, holding the title of Senator. Two of his sons and Napoleone were also Senators. Matteo ousted the traditional rivals, the Colonna, from Rome and extended the Orsini territories southwards up to Avellino and northwards to Pitigliano. During his life the family entered firmly in the Guelph party. He had some ten sons, which divided the fiefs after his deaths: Gentile (died 1246) originated the Pitigliano line and the second southern line, Rinaldo that of Monterotondo, Napoleone (died 1267) that of Bracciano and another Matteo Rosso that of Montegiordano, from the name of the district in Rome housing the family's fortress. The most distinguished of his sons was however Giovanni Gaetano (died 1280): elected pope as Nicholas III, he named the nephew Bertoldo (died 1289) as count of Romagna and had two nephews and a brother created cardinals.
The second southern line
The rise of the Orsini did not stop after Nicholas' death. Bertoldo's son, Gentile II (1250-1318), was two times Senator of Rome, podestà of Viterbo and, from 1314, Gran Giustiziere ("Great Justicer") of the Kingdom of Naples. He married to Clarice Ruffo, daughter of the counts of Catanzaro, forming an alliance of the most powerful Calabrian dynasty. His son Romano (1268-1327), called Romanello, was Royal Vicar of Rome in 1326, and inherited the countship of Soana through his marriage with Anastace de Montfort. Romano's stance was markedly Guelph. After his death, his two sons divided his fiefs, forming the Pitigliano and the second southern line.
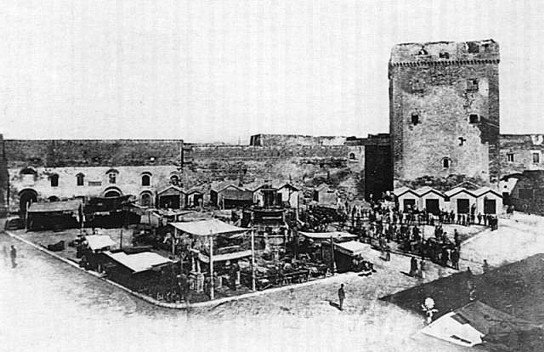
The Tower of Raimondello Orsini in Taranto, c. 1880.
Roberto (1295-1345), Gentile II's elder son, married to Sibilla del Balzo, daughter of the Great Senechal of the Kingdom of Naples. Among his sons, Giacomo (died 1379) was created cardinal by Gregory XI in 1371, while Nicola (August 27, 1331 - February 14, 1399) obtained the counties of Ariano and Celano. The latter was also Senator of Rome and enlarged the family territories in Lazio and Tuscany. His second son, Raimondello Orsini del Balzo, supported Charles III' coup d'état in Naples against Queen Joan II. Under king Ladislas he was among the few Neapolitan feudatories who were able to maintain their territorial power after the royal war against them. However, at his death in 1406 the southern Orsini fiefs were confiscated. Relationships with the royal family remained cold under Joan II; however, when Raimondello's son Giannantonio (1386-1453) sent his troops to help her against the usurpation attempt of James of Bourbon, he received in exchange the Principality of Taranto.
The links with the court increased further under Sergianni Caracciolo, Joan's lover and Great Senechal. A younger brother of Giannantonio one of Sergianni's daughters. However, the Orsini changed side when Alfonso V of Aragon started his conquest of the Kingdom of Naples. Giannantonio was awarded with the duchy of Bari, the position of Great Connestable and an appanage of 100,000 ducati. Giannantonio remained faithful to Alfonso's heir, Ferdinand I, but was killed during a revolt of nobles. Having died withouot legitimate sons, much of his were absorbed into the Royal Chamber.
Pitigliano line
This line was initiated by Guido Orsini, second son of Romano, who inherited the county of Soana. He and his descendants ruled over the fiefs of Soana, Pitigliano and Nola, but in the early 15th century wars against the Republic of Siena and the Colonnas caused to lost of several territories. Bertoldo (died 1417) managed to keep only Pitigliano, while his grandson Orso (died July 5, 1479) was count of Nola and fought as condottiero under the Duke of Milan and the Republic of Venice. Later he passed to the service of Ferdinand I of Naples, but, having not took part to the Barons' conjure, was rewarded with the fiefs of Ascoli and Atripalda. He took part to the Aragonese campaign in Tuscany and was killed in the siege of Viterbo.

Gerolama Orsini, Pier Luigi's wife.
The most outstanding member of the Pitigliano line was Niccolò, one of the major condottieri of the time. His son Ludovico (died January 27, 1534) and his nephew Enrico (died 1528) took part to the Italian Wars at the service of both France and Spain, often changing side with the typical ease of the Italian military leaders of the time. Two of Ludovico's daughter married to relevant figures: Geronima to Pier Luigi Farnese, illegitimate son of Pope Paul III, and Marzia to Gian Giacomo Medici of Marignano, an important general of the Spanish army.
The line started to decay after the loss of Nola by Ludovico, who was also forced to accept the Senese suzerainty over Pitigliano. Under his son Giovan Francesco (died May 8, 1567) the county enter in the orbit of the Grand Duke of Tuscany. Later, the attempt of Alessandro (died February 9, 1604) to obtain the title of Monterotondo was thwarted by Pope Gregory XIII. His son Giannantonio (March 25, 1569 - 1613) sold definitely Pitigliano to Tuscany, in exchange to the marquisate of Monte San Savino. The line became extinct in 1640 with the death of Alessandro.
Monterotondo line
This line was founded by Rinaldo, third son of Matteo Rosso the Great. They were often involved in the baronal struggles of the Late Middle Ages Rome, at least three members of the family being elected as Senators, while others fought as condottieri. Francesco in 1370 took part to the war of Florence against the Visconti of Milan. Orso (died July 24, 1424) died fighting for the king of Naples in the Battle of Zagonara against the Milanese. His sons Giacomo (died 1482) and Lorenzo (1452) battled for the Papal States, Naples and Florence. One of Giacomo's daughters, Clarice (1453–July 30, 1488) became Lorenzo de' Medici's wife. Franciotto Orsini was created cardinal by Leo X in 1517.
The most important member of the Monterotondo Orsinis was Giovani Battista Orsini, who became cardinal under Sixtus IV (1483). He was probably among the promoters of the failed plot against Cesare Borgia in 1502, being assassinated as retaliation, together with numerous members of the family.
The line decayed from the late 16th century, when several members were assassinated or lost their lands for various reasons. Its last representant Enrico (died September 12, 1643) and Francesco (1592 - September 21, 1650) sold Monterotondo to the Barberini in 1641.

The Orsini Castle in Nerola (Rome)
Bracciano line
Napoleone, another son of Matteo Rosso the Great, received Bracciano, Nerola and other lands in what is now northern Lazio. In 1259 he was Senator of Rome. Thanks to the strategic positions of their fiefs, and to their famous castle built in Bracciano in 1426, they were the most powerful Orsini line in the Lazio. Count Carlo (died after 1485), son of another Napoleone (died October 3, 1480), was Papal Gonfaloniere. By his marriage with a Francesca Orsini of Monterotondo was born Gentile Virginio Orsini, one of the most relevant figures of Italian politics in the late 15th century. After Carlo's death, he enlarged the family's tenure with lands inherited by his wife, another Orsini from Salerno, and most of all he was amongst the favourites of Ferdinand I of Naples, who appointed him as Great Connestable of Naples. Together with his cousin, the Cardinal Giovanni Battista, he was among the fiercest opposers of popes Innocent VIII and Alexander VI. In 1492 Gentile Virginio bought the county of Anguillara from Franceschetto Cybo.
During Charles VIII of France's descent into Italy, he managed to keep Bracciano by fighting without too much dogging against him. Ferdinand II had his fiefs confiscated and imprisoned him in Castel dell'Ovo, where he was poisoned in 1497. The family recovered this setback under the more friendly Medici popes of the early 16th century. His son Giangiordano was Prince Assistant to the Papal Throne. His son Virginio was a famous admiral for the Papal States and France, but in 1539 he had his fiefs confiscated under the charge of treason.
Paolo Giordano was created first Duke of Bracciano in 1560. An accomplished condottiero, he was however also a ruthless figure who had his wife Isabella de' Medici murdered. For this and other homicides he had to flee to northern Italy. He was succeeded by Virginio, whose heir Paolo Giordano II married the princess of Piombino and was created Prince of the Holy Roman Empire. His brother Alessandro was cardinal and Papal legate, and another brother, Ferdinando (died March 4, 1660) acquired the assets of the other line of San Gemini. In the 17th century the Dukes of Bracciano moved their residence to Rome. This, along with a general economical decadence, damaged the dukedom, and last Duke and Prince, Flavio (March 4, 1620 - April 5, 1698) was forced by the huge debts to sell it to the Odescalchi and others.
Gravina line
The line of Gravina, from the name of the eponymous city in Apulia, is the only existing line of the Orsini. It descends from Francesco (died 1456), a son of Count Carlo of Bracciano. Most of his fief were located in northern Lazio, but he entered in the Neapolitan orbit when in 1418 he was called by Sergianni Caracciolo to fight against the Angevine troops, which he defeated. By marriage, he obtained the title of count of Gravina. He was made Duke of Gravina by King Alfonso, title definitely assigned to his son Giacomo (died 1472), to which had been added the counties of Conversano, Campagna and Copertino. Two of Francesco's son, Marino (died 1471) and Giovanni Battista (died June 8, 1476), were respectively archbishop of Taranto and Grand Master of Knights of Rhodes.
The fourth duke, Francesco, was strangled by Cesare Borgia in 1503. One of his nephews, Flavio Orsini, was created cardinal in 1565. The fifth duke, Ferdinando (died December 6, 1549) had all his fiefs confiscated by the Spaniards, but regained it after a 40,000 scudi payment.
After the heirless death of Duke Michele Antonio (January 26, 1627), his lands passed to his cousin Pietro Orsini, count of Muro Lucano (died 1641). The latter's nephew Pier Francesco, who had renounced to the succession in favour to his brother Domenico to became a Dominican, was later elected pope with the name of Benedict XIII.
His successor raised Benedict XIII's nephew, Prince Beroaldo Orsini, to the dignity of Prince Assistants to the Papal Throne (title held until 1958), after the emperor Charles VI had already, in 1724, made him a prince of the Holy Roman Empire. The last cardinal from the family was Domenico.
The family moved to Rome in the 18th century, where Duke Domenico (November 23, 1790 - April 28, 1874), married Maria Luisa Torlonia in 1823. In 1850 he was Minister of War and General Lieutenant of the Papal Armies, and Senator of Rome as well.
The descendants of the family live in Rome, Torino, Singapore and in the United States. In the US there are a few people with the last name Orazine, the name was changed when family members emigrated to the United States due to translation difficulties. However, some still maintain the proper Orsini name.
Notable buildings
Apart the Bracciano castle, other notable buildings and structures associated with the Orsini include:
The Bomarzo Garden, a Late Renaissance-Mannerist gallery of bizarre sculptures and architecture commissioned in the 16th century by Vicino Orsini. It includes also a palace, designed by Baldassarre Peruzzi, begun in 1525 by Gian Corrado Orsini and finished by his son Vicino.
The Orsini Palace in Rome, including the Theatre of Marcellus.
Palazzo Orsini Pio Righetti, also in Rome.
Orsini Castles in: Avezzano, Nerola, Sant'Angelo Romano (15th century), Soriano nel Cimino (built by Nicholas III in 1278), Vasanello (12th century).