Lessico
Sedano di monte
Ligustico
Ligusticum officinale
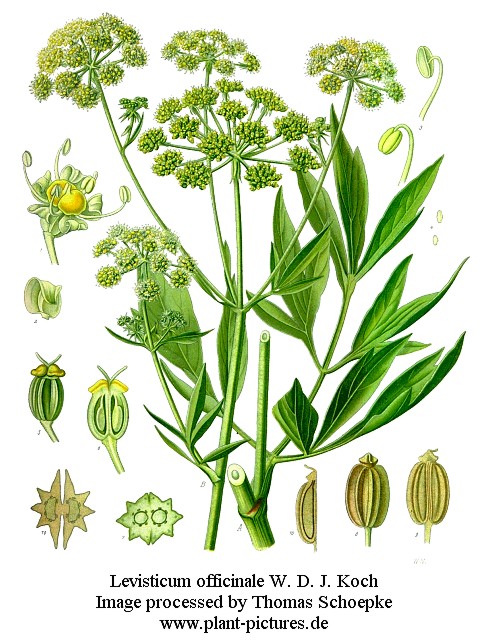
Dal latino ligusticum e dall’aggettivo greco neutro ligystikón, quindi, della Liguria, che in greco e in Aristotele suona Ligystikë. Per alterazione del latino ligusticum ne è scaturito levisticum, per cui in alcuni testi il Ligusticum officinale viene riportato come Levisticum officinale.
Il genere Ligusticum appartiene alla famiglia delle Ombrellifere, con circa 50 specie. Sono erbe perenni di varie parti del mondo. In Italia esistono 5 specie, tra cui il Ligusticum mutellina, la motellina o meo delle Alpi, detto anche Meum mutellina: si tratta di una pianta alta 50 cm con fiori bianchi o rosei, comune nei prati e nei pascoli di montagna, molto aromatica e appetita dal bestiame, specialmente bovino. La sua radice è usata nella medicina popolare ed è dotata di proprietà digestive, colagoghe e diuretiche.
Anche il Ligusticum officinale - o sedano di monte - è presente nella flora spontanea italiana ed è anche usato come pianta ornamentale. Le foglie emanano un delicato aroma se strofinate e vengono quindi impiegate per aromatizzare insalate, essendo il loro sapore pungente una via di mezzo tra quello del sedano e del prezzemolo. Può raggiungere i 2 m di altezza.
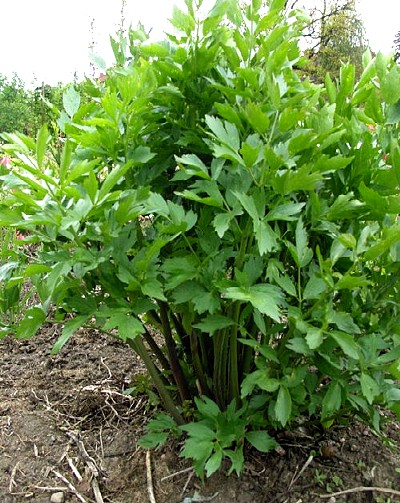


Lovage (Levisticum officinale) is a plant, the leaves and seeds or fruit of which are used to flavor food, especially in South European cuisine. It is a tall (3 to 9 ft) perennial that vaguely resembles its cousin celery in appearance and in flavor. Lovage also sometimes gets referred to as smallage, but this is more properly used for celery.
The fruit of the lovage plant can be used as a spice, but what appears in the trade as lovage seed is usually ajwain, not lovage. On the other hand, what is sold as 'celery seed' is often partially or entirely ground lovage seed.
The root of lovage, which is a heavy, volatile oil, is used as a mild aquaretic. Lovage root contains furanocoumarins which can lead to photosensitivity. Lovage is considered a "magic bullet" companion plant; much as borage helps protect almost all plants from pests, so lovage is thought to improve the health of almost all plants.
In Germany and Holland, one of the common names of Lovage is Maggikraut (German) or Maggiplant (Dutch) because the plant's taste is reminiscent of Maggi soup seasoning. In Romania the common name of Lovage is Leustean.
Lovage tea can be applied to wounds as an antiseptic, or drunk to stimulate digestion. Lovage is second only to capers in its quercetin content.
